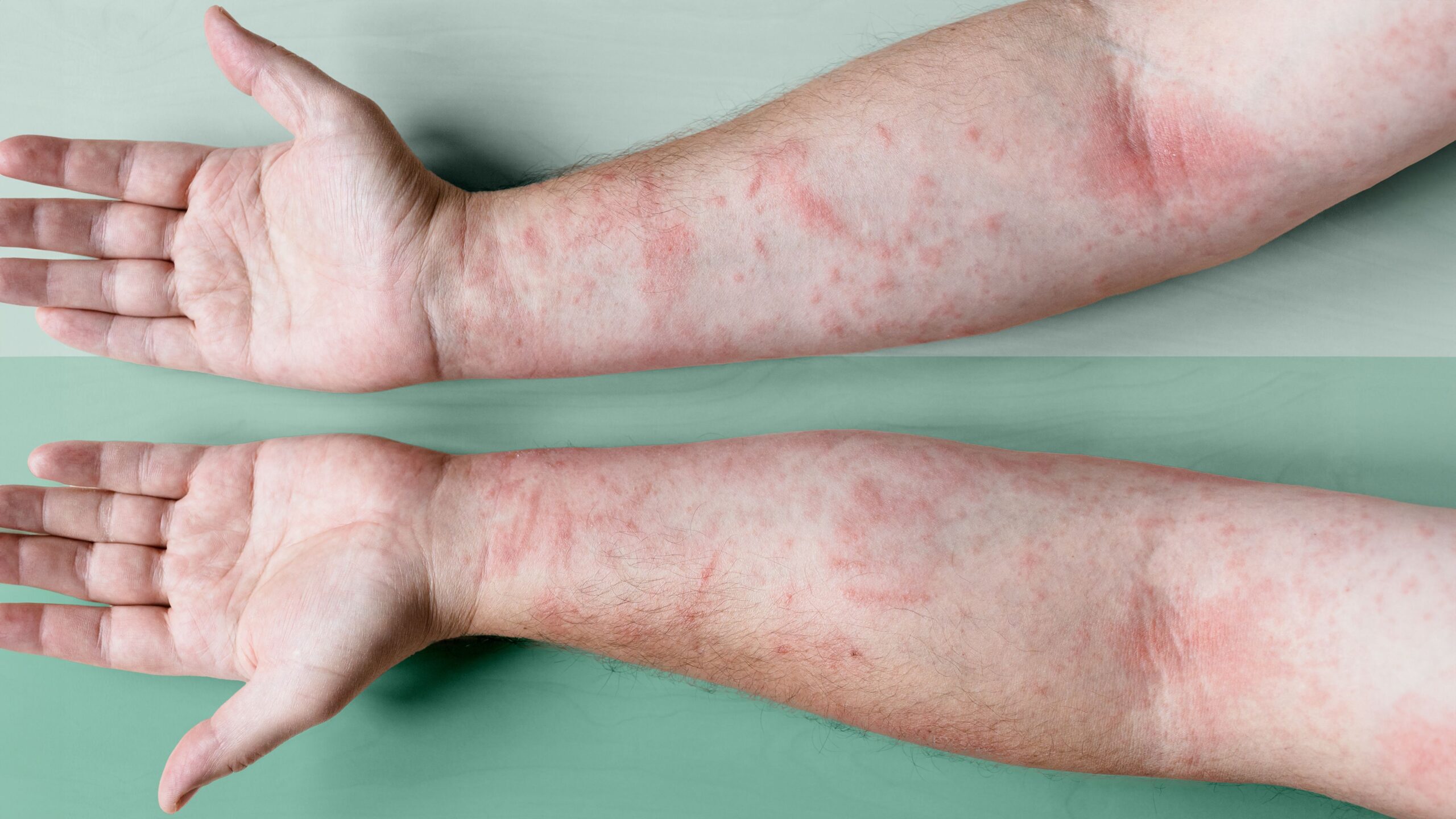
You’ve finally gotten your severe eczema under control. Those dry, itchy, unsightly lesions are gone — at least for the most part. In their place is discolored skin known as pigmentation.
These pigmented ghosts of eczema patches may be darker or lighter than the surrounding skin. They can be annoying to have to deal with, even though they’ll disappear in time.
“Most people find that when their eczema goes away, it does leave some type of mark behind, but it’s temporary,” says Marisa Garshick, MD, an assistant clinical professor of dermatology at Weill Cornell Medical Center and dermatologist at MDCS Dermatology in New York City.
As temporary as it may be, depending on how long the original patch was there, the pigmentation could take weeks or months to go away.
Follow our guide to treating this stubborn severe eczema symptom.
Why Severe Eczema Can Leave Pigmentation
Why does severe eczema lead to pigmentation in the first place? The answer lies in eczema’s underlying culprit, inflammation. Inflammation is a normal immune response to infection or injury but can sometimes be mistakenly triggered. This can lead to changes in the skin, such as patches of atopic dermatitis and the pigmentation that follows.
Atopic dermatitis can lead to two types of skin changes:
- Hyperpigmentation is when the skin becomes darker than the overall skin tone. “In eczema, it’s related to inflammation that has been there either from the primary process of eczema or from scratching and creating marks,” Dr. Garshick says.
- Hypopigmentation is when the skin looks lighter than the overall skin tone. This generally occurs when an eczema flare-up is resolving. Hypopigmentation may also be due to pityriasis alba, a condition related to eczema that can appear as lighter marks on the skin, she notes.
What You Can Do to Manage and Treat Pigmentation
If the eczema is fairly well controlled, a dermatologist may suggest straightforward treatments to ease pigmentation, such as:
- Exfoliation (e.g., with ammonium lactate)
- Moisturizers
- Products with oleic acid
You may not be concerned with how hyperpigmentation looks on your skin, but it’s still good to treat and manage it to reduce the overall amount of inflammation. Even after the severe eczema has been treated, your doctor may have you stop using topical steroids, which can cause permanent hypopigmentation if used for too long.
To avoid future flares and pigmentation issues, you’ll also want to be mindful of common triggers that can exacerbate hyperpigmentation. Try these ways of avoiding pigmentation or stopping it from getting worse:
- Skip heavy fragrances. Soaps, lotions, and perfumes with fragrances contain chemical compounds that can irritate your skin. This irritation can not only lead to an eczema flare, but also worsen existing pigmentation you may have. Some products labeled “fragrance-free” or “unscented” may still have compounds that mask the smell of the product. When in doubt, check for personal care products with the NEA’s Seal of Acceptance.
- Avoid certain clothing. Wool, nylon, and polyester fabrics can cause irritation, overheating, and sweating. Instead, opt for clothes that are 100 percent cotton or made with soft, breathable materials such as silk or bamboo. Itching and scratching skin can worsen pigmentation and prolong healing time.
- Apply (and reapply) sunscreen. It’s also important to wear sunscreen — even if your skin is naturally darker or you aren’t spending much time outside. “When the skin is already discolored, it’s more likely to become sensitive to the sun,” Garshick explains. People with severe eczema tend to do best with mineral sunscreens.
The Bottom Line for Hyperpigmentation: Keeping Eczema Under Control
- Injectable medications, such as biologics
- Oral medications that control inflammation
- Topical treatments, such as steroids or tretinoin
- Light therapy
- Moisturizers
If you have eczema that is leaving behind pigmentation, talk to your dermatologist, as it tends to be harder to treat pigmentation than eczema. “We want to get ahead of the eczema and make sure that we’re preventing the spots from forming in the first place,” Garshick explains.
If you’re currently experiencing a flare, you may already be seeing your dermatologist on a monthly basis or every few weeks. If your skin is calm and under good control, you may only have appointments when the seasons change.
Either way, it’s a good idea to check in if you have pigmentation, so you can get your skin to its healthiest.
The Takeaway
Dealing with pigmentation from severe eczema can be frustrating, but it’s a temporary skin change resulting from inflammation. Dark or light marks that fade over time are common, and using gentle skin-care routines, moisturizers, and sun protection can help. To prevent future or worsening pigmentation issues, managing severe eczema effectively is key.